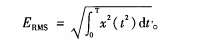Material deformation, damage and fracture process of energy accumulation and release process, when the local damage of material or fracture damage, energy is released in the form of stress wave, this is the phenomenon of acoustic emission (AE) [1]. Acoustic emission signal is received by the sensor materials in stress deformation damage when sound waves, the preamplifier, signal conditioners, processing and display of electrical signals, such as its frequency is mainly focused on the 100 kHz to 1 MHz. By AE technology to waveform signal extraction and processing, can analyze the material, the material deformation, the internal structure of mesoscopic change deformation expansion and deformation or fracture macroscopic changes completely [2-3]. Acoustic emission technology to real-time monitor damage process as the characteristic, can online monitoring of crack initiation and propagation process, is a kind of effective check dynamic defects NDT methods.
Wood based composite materials under external load matrix crack happens, interfacial debonding, delamination and fiber breakage form of microscopic damage, with the accumulation of time, eventually lead to the destruction of the material on the macroscopic [4]. Wood based composite materials in the process of damage fracture have a wealth of acoustic emission signals, through the collection and analysis of acoustic emission
1 materials and methods
1 material 1.
Selection of the commonly used wood composite plywood (11 layer, adjacent LVL wood grain direction perpendicular) and three polyurethane rubber cover particieboard two materials as the test materials, were 0.65, 0.696 cm3 density, made specifications for 300 mm (L) x 20 mm (T) x 18 mm (R) of the specimen, dry specimen at room temperature to stable moisture content is between 8% and 10%, in each set of specimens of 10.
1. 2 test method
Using acoustic emission instrument (changsha PengXiang PXWAE) and universal mechanical testing machine (shenzhen new think CMT 4204), the combination of the three point bending specimens for lateral pressure, loading speed for 5 MRN/min, when the specimen began to stress, acoustic emission instrument also began to collect acoustic emission signal [8]. Sensor model for the PXR - 15, resonance frequency is 150 kHz, sensor fixed on the specimen surface and with thick mixture to close, make the good contact with the specimen. Sensor receives the acoustic emission signal, transmission to the preamplifier, again through regulating device and microcomputer equipped with acoustic emission acquisition card collection and acoustic emission signal is displayed on the display and record. Acoustic emission signals were collected to make use of Matlab7.0 noise processing [9], and using the method calculating the main parameters of acoustic emission signal parameters, amplitude, effective voltage (RMS), ringing a total number,
The cumulative energy signal characteristic value, etc.
2 the results and analysis
2.1 active display
Load under the condition of the acoustic emission signal due to deformation and local stress, the range of the acoustic emission signal, effective signal such as voltage, ringing a total number, the accumulative energy eigenvalues can be respectively from two aspects of activity and damage reflect wood-based composites [10-15] internal damage evolution process. Ringing in total number, the accumulative energy value can be clearly shows that the acoustic emission signal characteristics, such as the damage of the specimens activity. Plywood deflection and the load of the specimens, ringing a total number and total energy relations as shown in figure 1.
Specimen in less than 3 mm deflection has not occurred when the acoustic emission phenomenon, the deflection increases to 3.2 mm or so acoustic emission phenomenon, and a steady increasing trend, main show is ringing total number and total energy increases slowly. When the deflection specimen 7 mm or so, the accumulative energy increases rapidly, specimen fracture. Later, as the crack extension, ringing the accumulative total and energy will increase slowly, fracture cracks appear "" word shape. Faced chipboard deflection and the load of the specimens, ringing count and tired
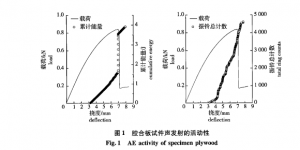
The relationship between energy and meter as shown in figure 2.
Compared with plywood specimens, faced chipboard specimen acoustic emission activity, has the following characteristics: (1) faced chipboard acoustic emission occurs early in plywood, deflection about the 2.1 mm audio emission phenomena occur, veneered particleboard early no acoustic emission process of slow increase, its ringing the accumulative total and energy are quickly increased to a certain number, and significantly reduce total ringing count than plywood, plywood ringing a total number of about 4890, compared with 136 faced chipboard. The reasons for this phenomenon may be experiment faced chipboard for three polyurethane glue stick panel, on the surface of brittle and no toughness, prone to fracture.
(2) faced chipboard acoustic emission phenomenon occurs, the accumulative energy can rapidly increase of 2.3 J, over time, energy and the process of slow increase, which suggests that faced chipboard under surface under the action of tensile stress fracture quickly, later, with the increase of the fracture surface and internal crack expanding faced chipboard. (3) faced chipboard specimen begins to break the deflection is only 2. 1 mm, the deflection and plywood up to 7 mm, it showed that the occurrence of micro cracks faced chipboard, extension, throughout the development process of very quickly, the fracture mechanism belongs to the ductile fracture.
2.2 damage characteristic
Amplitude is the maximum peak amplitude of the acoustic emission signal waveform, usually
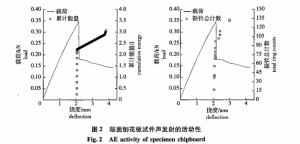
Expressed in decibels (dB). In terms of a mechanical point of view, and can be expressed in amplitude size of acoustic emission signal energy. ERMS is effective voltage RMS of the amplitude of the acoustic emission signal voltage sampling time, if a set of alternating
Voltage x (t), the effective voltage equation can be represented as [M] :
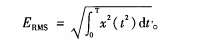
Also can think ERMS of acoustic emission wave power relative, is associated with the energy of acoustic emission signal, mainly used for the evaluation of acoustic emission
The number of active.
Figure 3 for plywood acoustic emission signal amplitude, the distribution of effective voltage with deflection and its intensity can directly reflect the frequency of acoustic emission events. The figure 3 shows that
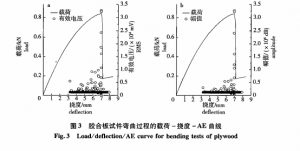
Plywood under the condition of three point bending specimen, and its internal injury, evolution, extension until the fracture process can be roughly divided into three stages: stage 1 linear elastic deformation stage, this stage does not appear acoustic emission signal, no damage; Nonlinear deformation stage, the stage 2 in the first half of the stage, only a small amount of low energy of acoustic emission signal, this shows that the micro cracks in the material, does not increase with the increase of load, and then half stage with micro crack formation and propagation, the acoustic emission signal gradually rich, until close to the limit load; Stage 3 ductile fracture stage, with the further increase of load, wood fiber bundle fracture pulled up, micro crack extension into macroscopic crack, unsteady expansion later on. Eventually lead to sudden rupture, releasing a large number of high-energy elastic energy, until the acoustic emission signal amplitude, maximum effective voltage. Compared with plywood, veneered particleboard shows that acoustic emission signal
(figure, faced chipboard damage until the fracture is roughly divided into two sections: the first phase is linear elastic stage, this stage does not appear sound signal, no damage; phase 2 is the fracture toughness stage, this stage acoustic emission signal amplitude and effective voltage quickly reached maximum, materials from the crack formation to the sudden rupture, releasing a large amount of elastic energy. Since then, with the increase of deflection, and the effective voltage amplitude reduced rapidly, indicating that with the increase of material, material particles are still in the acoustic emission signal, the low energy released material cracks continue to expand.
Theory of "three
(1) the occurrence of micro cracks faced chipboard, extension, throughout the development process is very rapid, it belongs to the ductile fracture mechanism fossa fracture, and fracture occurred significantly earlier than plywood.
(2) plywood damage stage mainly divided into: linear elastic stage, nonlinear deformation stage, stage of fracture toughness. Faced chipboard
Damage to the stage mainly divided into stages of linear elastic and fracture toughness.